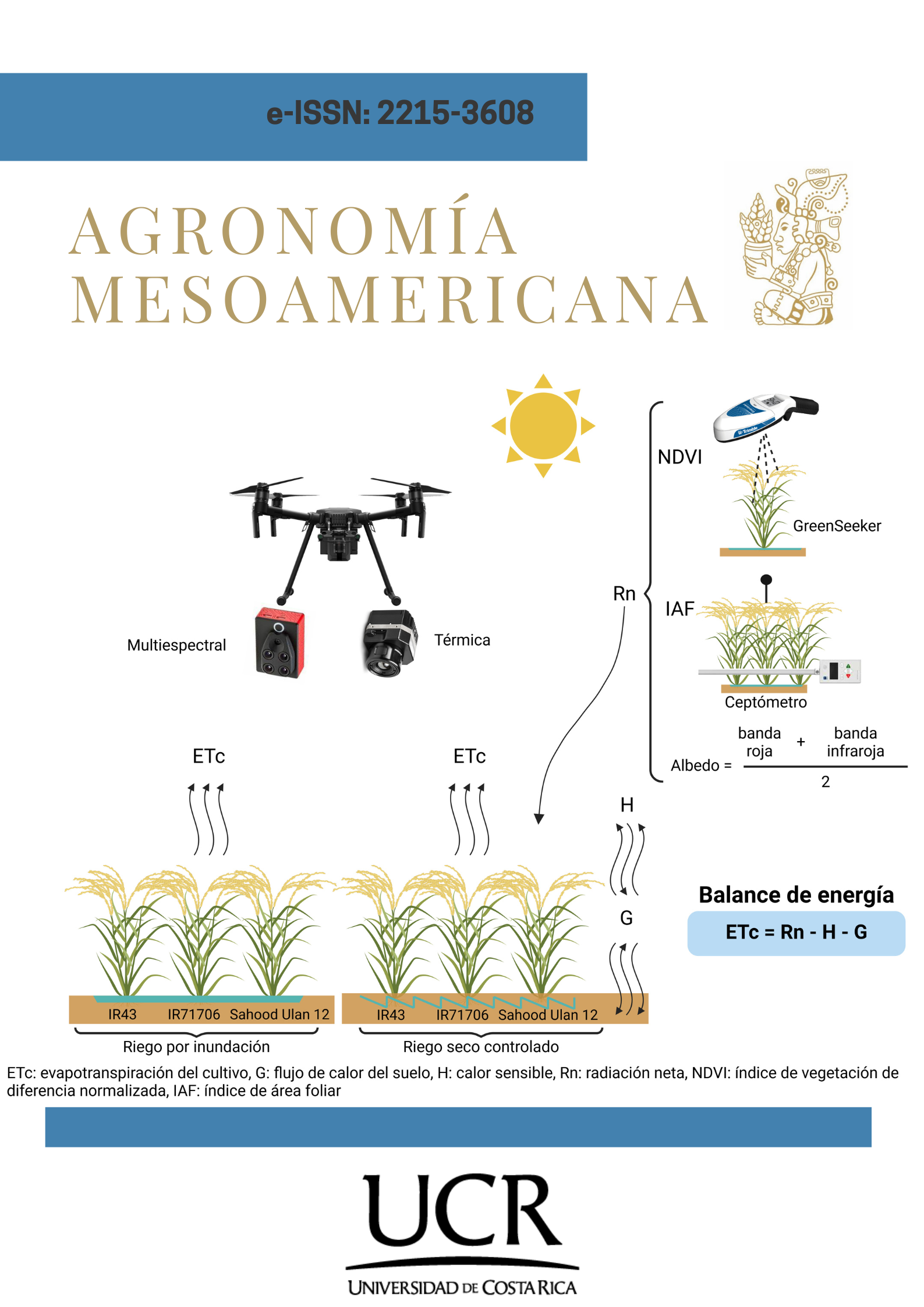
Use of RPAS for precision evapotranspiration in rice fields and water consumption reduction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15517/am.2024.56529Keywords:
rice paddies, energy balance, drone, controlled dry irrigationAbstract
Introduction. Estimating crop evapotranspiration (ETc) helps determine water requirements, enabling the proposal of irrigation techniques that save water. Objective. To use remotely piloted aircraft system (RPAs) for greater precision in measuring evapotranspiration in rice fields, aiming to reduce water consumption. Materials and methods. The study utilized a randomized complete block design with a factorial structure of two experiments: flooded irrigation (E1) and irrigation with controlled drying (E2), and three rice varieties (IR43, IR71706, Sahod Ulan 12). The study was conducted at the Experimental Irrigation Area (AER) of the Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina, Peru. Eight RPAS flights were carried out between January and February 2019, distributed between the tillering and cotton point stages. Results. The combined analysis of treatments using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s test with p < 0.05 revealed a significant difference in ETc between E1 and E2. However, no significant difference was found between the rice varieties. Maximum values of ETc and yield were obtained for E1 at 4.50 mm/ day and 10389 kg/ha, and for E2 at 3.7 mm/day and 9710 kg/ha, respectively. Conclusions. The use of a remotely piloted aircraft system improved the temporal and spatial resolution of multispectral and thermal images, providing greater accuracy in crop evapotranspiration (ETc) under two irrigation regimes. Controlled drying irrigation resulted in a A 24% reduction in ETc, allowing for a water saving of 855 m3/ha.
Downloads
References
Abebe, T., Alamerew, S., Tulu, L. (2017). Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance for yield and its related traits in rainfed lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes at Fogera and Pawe, Ethiopia. Advances in Crop Science and Technology, 5, Article 272. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-8863.1000272
Acharya, B., & Sharma, V. (2021). Comparison of satellite driven surface energy balance models in estimating crop evapotranspiration in semi-arid to arid inter-mountain region. Remote Sensing, 13(9), Article 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091822
Allen, R. G., Tasumi, M., & Trezza, R. (2007). Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—model. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 133(4), 380–394. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:4(380)
Anupoju, V., & Kambhammettu, B. (2020). Role of deficit irrigation strategies on ET partition and crop water productivity of rice in semi-arid tropics of south India. Irrigation Science, 38, 415–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-020-00684-1
Bian, J., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Chen, H., Cui, C., Li, X., Chen, S., Fu, Q. (2019). Simplified evaluation of cotton water stress using high resolution unmanned aerial vehicle thermal imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(3), Article 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030267
Castañeda-Ibáñez, C. R., Flores-Magdaleno, H., Martínez-Menes, M., Esparza-Govea, S., Fernández-Reynoso, D., Prado-Hernández, V., Pascual-Ramírez, F. (2018). Estimación de la evapotranspiración mediante un balance de energía utilizando sensores remotos. Ecosistemas y Recursos Agropecuarios, 5(15), 537–545. https://doi.org/10.19136/era.a5n15.1647
Chandel, A. K., Molaei, B., Khot, L. R., Peters, R. T., & Stöckle, C. O. (2022). High resolution geospatial evapotranspiration mapping of irrigated field crops using multispectral and thermal infrared imagery with METRIC energy balance model. Journal of the. Drone, 4(3), Article 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones4030052
Cheng, H., Shu, K., Zhu, T., Wang, L., Liu, X., Cai, W., Qi, Z., & Feng, S. (2022). Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on yield, water and nitrogen use, and greenhouse gas emissions in rice paddy fields. Journal of Cleaner Production, 349, Article 131487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131487
Chu, G., Chen,T., Chen, S., Xu, C., Wang, D., & Zhang, X. (2018). The effect of alternate wetting and severe drying irrigation on grain yield and water use efficiency of Indica-japonica hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.). Food and Energy Security, 7(2), Article e00133. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.133
Djaman, K., Rudnick, D. R., Moukoumbi, Y. D., Sow, A., & Irmak, S. (2019). Actual evapotranspiration and crop coefficients of irrigated lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) under semiarid climate. Italian Journal of Agronomy, 14(1), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.4081/ija.2019.1059
Durán Gómez, M. R., Ramos Fernández, L., Altamirano Gutiérrez, L., & Arapa Quispe, J. (2021). Thermal imaging and thermocouple sensors for estimating water stress index of rice cultivation under drip irrigation. Idesia (Arica), 39(1), 109–118. https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-34292021000100109
Fan, L., Gao, Y., Brück, H., & Bernhofer, C. (2009). Investigating the relationship between NDVI and IAF in semi-arid grassland in Inner Mongolia using in-situ measurements. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 95(1–2), 151–156. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0369-2
Fonseca Salazar, S., Verano Zelada, C., & Mariluz Silva, J. P. (2012, octubre 26). Huella hídrica del cultivo del arroz. Huella hídirca del arroz en el Perú. Oficina del Sistema Nacional de Información de Recursos Hídricos. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12543/546
Food and Agriculture Organization. (n.d.). FAOSTAT. Crop and livestock products. Retrieved February 23, 2022, from http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC
Folhes, M. T., Rennó, C. D., & Soares, J. V. (2009). Remote sensing for irrigation water management in the semi-arid Northeast of Brazil. Agricultural Water Management, 96(10), 1398–1408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2009.04.021
Hardin, P. J., & Jensen, R. R. (2011). Small-scale unmanned aerial vehicles in environmental remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 48(1), 99–111. https://doi.org/10.2747/1548-1603.48.1.99
Heros Aguilar, E. C., Lozano-Isla, F., & Casas Diaz, A. V. (2023). Tecnologías para la producción de arroz: recomendaciones para el Perú basadas en investigaciones científicas. South Sustainability, 4(1), Article e069. https://doi.org/10.21142/SS-0401-2023-e069
Hussain, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Yang, H., Arfan, M., Hassan, D., Wang, W., Azam, M. I., & Faisal, M. (2022). A comparative appraisal of classical and holistic water scarcity indicators. Water Resources Management, 36(3), 931–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03061-z
Ishfaq, M., Farooq, M., Zulfiqar, U., Hussain, S., Akbar, Ahmad, N., Nawaz, A., & Ahmad Anjum, S. (2020). Alternate wetting and drying: A water-saving and ecofriendly rice production system. Agricultural Water Management, 241, Article 106363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106363
Jiang, Y., Carrijo, D., Huang, S., Chen, J., Balaine, N., Zhang, W., van Groenigen, K. J., & Linquist, B. (2019). Water management to mitigate the global warming potential of rice systems: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Research, 234, 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.02.010
Kumar, A., & Rajitha, G. (2019). Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) irrigation - A smart water saving technology for rice: A review. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8(3), 2561–2571. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.803.304
Lee, Y., & Kim, S. (2016). The modified SEBAL for mapping daily spatial evapotranspiration of South Korea using three flux towers and terra MODIS data. Remote Sensing, 8(12), Article 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8120983
Liu, X., Xu, J., Yang, S., & Zhang, J. (2018). Rice evapotranspiration at the field and canopy scales under water-saving irrigation. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 130, 227–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0507-z
Machaca-Pillaca, R., Pino-Vargas, E., Ramos-Fernández, L., Quille-Mamani, J., & Torres-Rua, A. (2022). Estimación de la evapotranspiración con fines de riego en tiempo real de un olivar a partir de imágenes de un drone en zonas áridas, caso La Yarada, Tacna, Perú. Idesia (Arica), 40(2), 55–65. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-34292022000200055
Maresma, A., Chamberlain, L., Tagarakis, A., Kharel, T., Godwin, G., Czymmek, K., Shields, E., Ketterings, Q. M. (2020) Accuracy of NDVI-derived corn yield predictions is impacted by time of sensing. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 169, Article 105236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105236
Mendoza-Pérez, C., Ramírez-Ayala, C., Ojeda-Butamante, W., Flores-Magdaleno, H. (2017). Estimation of leaf area index and yield of greenhouse-grown poblano pepper. Ingeniería Agrícola y Biosistemas, 9(1), 37–50. https://doi.org/10.5154/r.inagbi.2017.04.009
Montibeller, Á. G. (2017). Estimating energy fluxes and evapotranspiration ofcorn and soybean with an unmanned aircraft system in Ames, Iowa [Master of Arts thesis, University of Northern Iowa]. UNI Scholar Works. https://scholarworks.uni.edu/etd/416
Neira Huamán, E., Ramos Fernández, L., & Razuri Ramírez, L. R. (2020). Coeficiente del cultivo (Kc) del arroz a partir de lisímetro de drenaje en La Molina, Lima-Perú. Idesia (Chile), 38(2), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-34292020000200049
Nassar, A., Torres-Rua, A., Kustas, W., Alfieri, J., Hipps, L., Prueger, J., Nieto, H., Alsina, M. M., White, W., McKee, L., Coopmans, C., Sanchez, L., & Dokoozlian, N. (2021). Assessing daily evapotranspiration methodologies from one-time-of-day sUAS and EC information in the GRAPEX project. Remote Sensing, 13(15), Article 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152887
Nhamo, L., Magidi, J., Nyamugama, A., Clulow, A. D., Sibanda, M., Chimonyo, V. G. P., & Mabhaudhi, T. (2020). Prospects of improving agricultural and water productivity through unmanned aerial vehicles. Agriculture, 10(7), Article 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10070256
Niu, H., Hollenbeck, D., Zhao, T., Wang, D., & Chen, Y. (2020). Evapotranspiration estimation with small UAVs in precision agriculture. Sensors, 20(22), Article 6427. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226427
Ortega-Farías, S., Ortega-Salazar, S., Poblete, T.; Kilic, A., Allen, R., Poblete-Echeverría, C., Ahumada-Orellana, L., Zuñiga, M., Sepúlveda, D. (2016). Estimation of energy balance components over a drip-irrigated olive orchard using thermal and multispectral cameras placed on a helicopter-based unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Remote Sensing, 8(8), Article 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080638
Ouda, S., & Zohry, A. E. H. (2022). Water-smart practices to manage water scarcity. In S. Ouda, & A. El-Hafeez Zohry (Eds.), Climate-smart agriculture (pp. 3–26). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93111-7_1
Porras-Jorge, R., Ramos-Fernández, L., Ojeda-Bustamante, W., & Ontiveros-Capurata, R. (2020). Performance assessment of the AquaCrop model to estimate rice yields under alternate wetting and drying irrigation in the coast of Peru. Scientia Agropecuaria, 11(3), 309–321. https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2020.03.03
Quille-Mamani, J., Ramos-Fernández, L., & Ontiveros-Capurata, R. (2021). Estimación de la evapotranspiración del cultivo de arroz en Perú mediante el algoritmo METRIC e imágenes VANT. Revista de Teledetección, (58), 23–38. https://doi.org/10.4995/raet.2021.13699
Roy, D., Hossain, M. B., Bin Hafiz Pranto, M. R., & Islam, M. T. (2022). Drought management by integrated approaches in T. Aman rice season to escalate rice productivity in drought prone regions of Bangladesh. In G. m. Terekul Islam, S. Shampa, & A. I. A. Chowdhury (Eds.), Water management: A view from multidisciplinary perspectives (pp. 351-364). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95722-3_17
Saha, S., Ahmmed R., & Jahan, N. (2022). Actual evapotranspiration estimation using remote sensing: Comparison of Sebal and Metric models. In G. M Tarekul Islam, Shampa, & A. I. Amin Chowdhury (Eds.), Water management: A view from multidisciplinary perspectives (pp. 365–383). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95722-3_18
Sawadogo, A., Kouadio, L., Traoré, F., Zwart, S. J., Hessels, T., & Gündoğdu, K. S. (2020). Spatiotemporal assessment of irrigation performance of the Kou Valley irrigation scheme in Burkina Faso using satellite remote sensing-derived indicators. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(8), Article 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080484
Shabir, K., Kumar, R., & Maryam, M.(2023). Evapotranspirationin contest of climate change: Evapotranspiration. In M. Kumar, R. Kumar, & V. P. Singh (Eds.), Advances in water management under climate change (1st ed., Capter 15, pp. 274–290). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003351672
Sisheber, B., Marshall, M., Mengistu, D., & Nelson, A. (2022). Tracking crop phenology in a highly dynamic landscape with knowledge-based Landsat–MODIS data fusion. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 106, Article 102670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102670
Suwanlertcharoen, T., Chaturabul, T., Supriyasilp, T., & Pongput, K. (2023). Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration Using Satellite-Based Surface Energy Balance Derived from Landsat Imagery in Northern Thailand. Water, 15(3), Article 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030450
Taherparvar, M., & Pirmoradian, N. (2018). Estimation of rice evapotranspiration using reflective images of Landsat satellite in sefidrood irrigation and drainage network. Rice Science, 25(2), 111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2018.02.003
Tsouni, A., Kontoes, C., Koutsoyiannis, D., Elias, P., & Mamassis, N. (2008). Estimation of actual evapotranspiration by remote sensing: Application in Thessaly plain, Greece. Sensors, 8(6), 3586–3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8063586
Villar Barraza, H. D., Ramos Fernández, L., & Alminagorta Cabezas, O. (2021). Evaluación del estrés hídrico del cultivo de arroz (IR 71706) a través del uso de termografía calibrada del área del dosel en Lima, Perú. Idesia (Arica), 39(4), 59–70. https://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-34292021000400059
Wei, G., Cao, J., Xie, H., Xie, H., Yang, Y., Wu, C., Cui, Y., & Luo, Y. (2022). Spatial-temporal variation in paddy evapotranspiration in subtropical climate regions based on the SEBAL model: A case study of the Ganfu Plain irrigation system, southern China. Remote Sensing, 14(5), Article 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051201
Zobeidi, T., Yaghoubi, J., & Yazdanpanah, M. (2022). Farmers’ incremental adaptation to water scarcity: An application of the model of private proactive adaptation to climate change (MPPACC). Agricultural Water Management, 264, article 107528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107528
Zhou, S., Sun, H., Bi, J., Zhang, J., Riya, S., & Hosomi, M. (2020). Effect of water-saving irrigation on the N2O dynamics and the contribution of exogenous and endogenous nitrogen to N2O production in paddy soil using 15N tracing. Soil & Tillage Research, 200, Article 104610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104610
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 David Junior Quispe-Tito, Lia Ramos-Fernández, Edwin Pino-Vargas, Javier Quille-Mamani, Alfonso Torres-Rua

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. Proposed policy for open access journals
Authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. Authors retain the copyright and assign to the journal the right to the first publication, with the work registered under the attribution, non-commercial and no-derivative license from Creative Commons, which allows third parties to use what has been published as long as they mention the authorship of the work and upon first publication in this journal, the work may not be used for commercial purposes and the publications may not be used to remix, transform or create another work.
b. Authors may enter into additional independent contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (e.g., including it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book) provided that they clearly indicate that the work was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are permitted and encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (e.g. on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it may lead to productive exchanges and faster and wider dissemination of published work (see The Effect of Open Access).